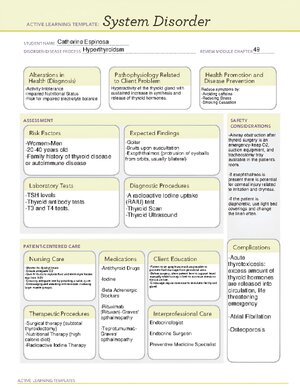
This document Money and Credit provides valuable insights into the concepts of money, credit, and banking systems. Exploring the significance of money as a medium of exchange, it delves into the evolution from barter systems to modern banking practices. Understanding credit terms, collateral, and sources in India is crucial for managing finances effectively. Learn about the role of formal and informal credit sectors, interest rates, and debt traps to make informed financial decisions. Ideal for Class 10 students studying social science, this document by Prashant Kirad offers a comprehensive overview of money, credit, and their impact on the economy.

_page_1-rcnx7518g6711dl41dsvglhmls4sd5521ooys8eo2g.webp)
_page_1-212x300.webp)